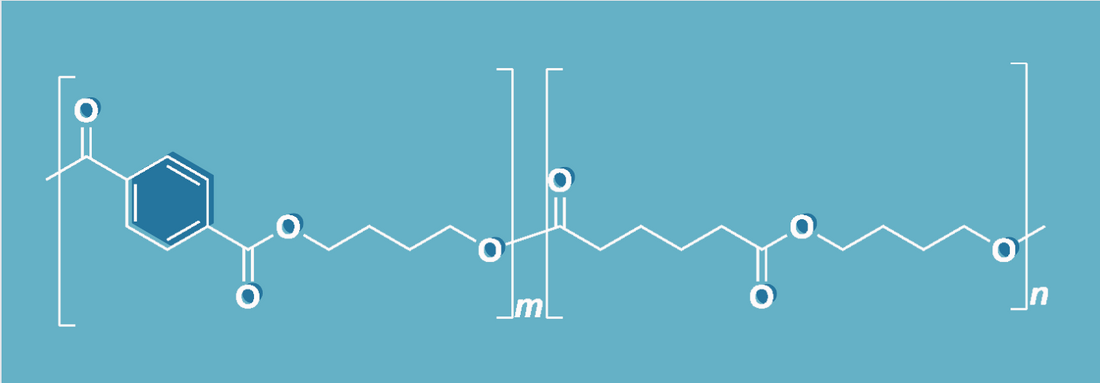
What is PBAT? PBAT (Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate) is a biodegradable and compostable plastic widely used in sustainable packaging solutions. It is known for its flexibility, strength, and ability to break down under composting conditions, making it an excellent alternative to traditional plastics.
How is PBAT Made? PBAT is synthesized through the polymerization of adipic acid, 1,4-butanediol, and terephthalic acid (Science Direct). This process creates a plastic material that is both durable and capable of decomposing in composting environments.
Why is PBAT Used in Compostable Film? PBAT is used in compostable films due to its excellent biodegradability and mechanical properties. It provides the necessary flexibility and strength for packaging applications while ensuring that the material can break down in composting facilities. This makes PBAT an ideal choice for eco-friendly packaging solutions that aim to reduce plastic waste and its impact on the environment.
Certifications and Environmental Safety Certifying bodies such as BPI, TUV, ABA, and DINCERTO rigorously test materials like PBAT for ecotoxicity, heavy metal contamination, and microplastics. These organizations ensure that using PBAT is safe for the environment by granting certifications only to materials that meet their stringent requirements
You can refer to the standards used by these certifying bodies to approve certifications, you'll find very specific requirements that must be met::
- Australia: AS 5810 (2010) – Biodegradable plastics suitable for home composting
- TUV: EN 13432 and Home Compost
- France: NF T 51800 (2015) – Plastics suitable for home composting
- Europe: EN 17427 (2022) - Requirements for carrier bags suitable for home composting
- USA: ASTM 6400 and 6868
Methane Production Concerns The methane production rate of PBAT is minimal, and while there are not extensive studies on this topic, PBAT is not considered a major contributor to methane emissions. A detailed study comparing the methane potential of PBAT/PLA to other polymers during degradation can be found in this paper from page 98 onwards.
Biodegradable Plastics in Landfills When biodegradable plastics like PBAT end up in landfills, they do not degrade optimally due to the lack of oxygen. Instead of biodegrading, they begin to rot along with other waste materials. However, the impact of a single bag in terms of mass is negligible compared to the overall organic waste in a landfill. This issue is not unique to PBAT but is a challenge for all biodegradable plastics in landfill conditions.
At EcoPackables, we are committed to staying at the forefront of sustainable packaging innovation. We are dedicated to bringing new materials like PBAT to market, ensuring that our clients have access to the best eco-friendly options available. By embracing these innovative materials, we can work together to reduce our environmental impact and help fund the next generation of sustainable materials. If you have more questions or want to explore our sustainable packaging solutions, contact EcoPackables today.